Git tricks & Deterministic builds on NPM install
Find the files in a git repository that have changed the most
With a few CLI tools along with the git log command, you can see the files that have changed the most over a certain time period.
I've set up a ZSH function in my .zshrc file
gitchangehist() {
git log --numstat |
awk '/^[0-9-]+/{ print $NF}' |
sort |
uniq -c |
sort -nr |
head
}I ran this on my website's codebase and here's the result
gitchangehist37 src/components/Layout/layout.css
31 gatsby-config.js
23 package.json
20 src/templates/post.css
19 yarn.lock
19 src/pages/index.js
14 content/posts/twitter-bot-tutorial-nodejs/index.md
12 src/pages/portfolio.js
11 src/components/Portfolio/Project.css
10 content/posts/what-does-it-mean-to-own-a-bitcoin/index.mdGit provides a convenient way to limit commits with the --since option.
--since=<date>, --after=<date>
Show commits more recent than a specific date.You can use it like this to pass in a time frame
git log --since 1.year.ago
git log --since 1.month.agoThere are also other interesting options like --author and --grep.
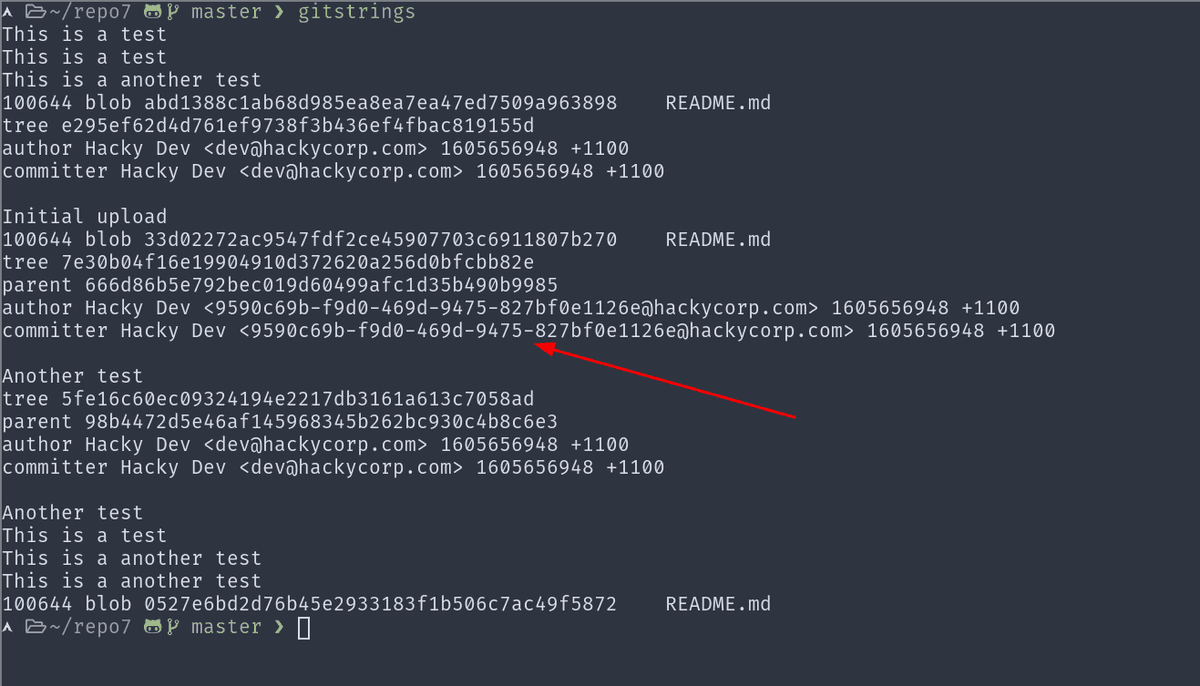
List all the strings inside a git repository
This is probably my favorite git trick provided by the awesome @TomNomNom
gitstrings() {
# Print all the strings in .git/objects/pack
# Credits to tomnomnom - https://twitter.com/tomnomnom/status/1133345832688857095
{
find .git/objects/pack/ -name "*.idx" | while read i; do git show-index <"$i" | awk '{print $2}'; done
find .git/objects/ -type f | grep -v '/pack/' | awk -F'/' '{print $(NF-1)$NF}'
} | while read o; do git cat-file -p $o; done
}
This one-liner will find all the strings in a git repo and just spit it out to the stdout. It's super useful especially to bug-bounty hunters to look for any leaked credentials or API keys. Sometimes developers commit confidential keys and then make another commit to remove them but git stores the entire history and this one-liner will help you find them.
I used this trick to basically glide through the Recon Badge in PentesterLab.
You can use interesting grep patterns to find some juicy stuff.
Deterministic NPM install
NodeJS' package manager npm keeps track of the dependency graph (the dependencies of the main dependencies and their dependencies and so on) in a package-lock.json file. This file is essential to have consistent versions of the dependencies. The next time we need to install dependencies, this file should help us get the right versions.
Sounds good right? Nope. The command, npm install, that most of us use, does not use the lock file at all! You may have noticed that when you run npm install the lock file gets changed. If a dependency is not in the package-lock.json it will be added by npm install.
The command you want to use is npm ci. It's named after Continuous Integration. If any dependencies are missing or have incompatible versions, it will throw an error.
 Source: https://stackoverflow.com/a/53325242/6199444
Source: https://stackoverflow.com/a/53325242/6199444
In my internship, I had to work on an Angular project but I just couldn't make it run. I probably should have used ci instead of install 😁.